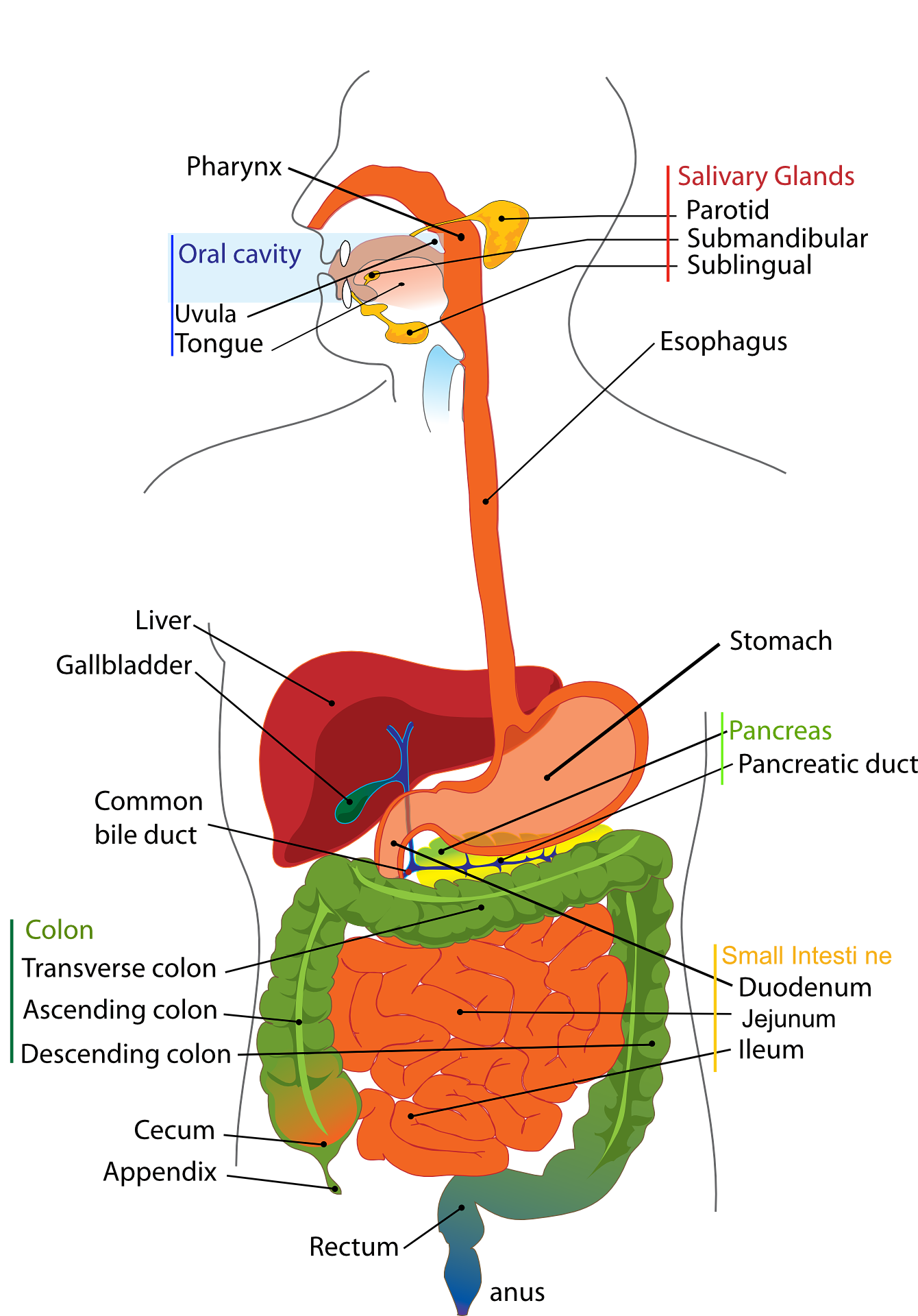
Pancreatic cancer, a complaint of abnormal cell growth in the pancreas, is one of the most grueling and deadly forms of cancer. With a fairly low survival rate, it's pivotal to deeply understand aspects related to this complaint, from symptoms and causes to individual styles, treatment options and preventative strategies. In this composition, we will dive into the colorful confines of pancreatic cancer in order to give a comprehensive overview of this complex medical challenge.
SYMPTOMS OF PANCREATIC CANCER
Pancreatic cancer is a multifaceted condition and frequently challenging to diagnose beforehand due to its tendency to remain asymptomatic in its early stages. As it progresses, still, the excrescence can manifest a variety of distinct symptoms, which can give important suggestions to relating and treating the complaint. In this member, we will explore in detail the characteristic symptoms associated with pancreatic cancer.
- Nausea and Vomiting: are symptoms frequently associated with pancreatic cancer, although they aren't specific to this complaint. The pancreas plays a pivotal part in producing digestive enzymes that help break down food. When a excrescence affects the normal functioning of the pancreas, digestion can be bloodied, performing in nausea and vomiting. These symptoms can be especially pronounced after refections and may contribute to the involuntary weight loss frequently seen in cases with pancreatic cancer.
- Abdominal Pain or Back Pain: Pain is one of the most common symptoms associated with pancreatic cancer. Cases frequently report abdominal pain or reverse pain, which can range in intensity from moderate to severe. Abdominal pain may be the result of excrescence growth or pressure wielded by the excrescence on bordering structures. As the excrescence develops, the pain tends to come more patient and enervating, which can significantly affect the case's quality of life.
- Jaundice: When the Skin and Eyes unheroic hostility is a hallmark symptom of pancreatic cancer, especially when the excrescence affects the head of the pancreas, where the common corrosiveness conduit is located. The blockage of the corrosiveness conduit by the excrescence prevents the proper inflow of corrosiveness, performing in the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. This causes a unheroic tincture to the skin and eyes, a symptom that's frequently conspicuous and that can prompt cases to seek medical help.
- Unintentional Weight Loss Unintentional: weight loss is a frequent concern among cases with pancreatic cancer. The excrescence can negatively affect the body's metabolism, leading to loss of muscle mass and fat, indeed when food input is maintained. This symptom can be aggravated by digestive dysfunction, nausea, and other cancer- related factors. pronounced weight loss can indicate advanced stages of the complaint.
- Enlarged Liver or Gallbladder: As pancreatic cancer progresses, there's a possibility that the excrescence may spread to bordering organs or to more distant spots in the body, in a process known as metastasis. This can lead to blowup of the liver or gallbladder, which can be detected through imaging tests. Blowup of these organs is frequently a sign that the complaint has reached more advanced stages.
- Blood Clot: Cases with pancreatic cancer have an increased threat of developing blood clots, also known as deep tone thrombosis. This is because cancer can beget changes in blood clotting, making the blood more likely to form clots. Blood clots pose a significant threat as they can travel to other corridor of the body, similar as the lungs, causing serious complications.
- Diabetes Mellitus: The relationship between pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus is complex. Diabetes can be both a cause and a symptom of pancreatic cancer. Cancer can occasionally affect the insulin- producing cells in the pancreas, leading to the development of diabetes. On the other hand,pre-existing diabetes can increase the threat of developing pancreatic cancer. This link underscores the interconnectedness between the conditions and the need for comprehensive assessment for cases.
CAUSES OF PANCREATIC CANCER
While the exact cause of pancreatic cancer isn't completely understood, several threat factors have been linked as implicit contributors to its development:
- Smoking: is one of the main threat factors for pancreatic cancer. Chemicals in tobacco can damage the DNA in pancreatic cells, adding the threat of cancerous mutations.
- Family History: Having first degree cousins with a history of pancreatic cancer or other affiliated cancers increases the threat of developing the complaint. This may be related to participated inheritable or environmental factors. Old age
- Old age: is a threat factor, as utmost cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed in people over 65 times old. This could be related to the accumulation of mutations over time.
- Obesity: is a threat factor that has been linked to an increased liability of developing pancreatic cancer. The relationship between rotundity and habitual inflammation may contribute to this association.
DIAGNOSIS OF PANCREATIC CANCER
Imaging Tests: Various imaging tests can help visualize the pancreas and identify any abnormalities. These tests may include:
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This is often one of the first tests done to look for tumors, assess their size and location, and check if cancer has spread to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI can provide detailed images of the pancreas and surrounding tissues, helping to determine the extent of the cancer.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with an ultrasound probe into the digestive tract to get detailed images of the pancreas and nearby structures.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scan: This scan can help identify areas of the body where cells are rapidly dividing, which can indicate cancer. It's often used in combination with other imaging tests.
- Biopsy: If imaging tests suggest the presence of a tumor, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. There are different ways to obtain a tissue sample, such as fine-needle aspiration (FNA) guided by imaging, endoscopic biopsy, or surgical biopsy. The tissue sample is then examined by a pathologist to determine if it's cancerous and, if so, what type of cancer it is.
- Blood Tests: Some blood tests may provide clues about the presence of pancreatic cancer or its effects on the body. For instance, elevated levels of certain enzymes and tumor markers may suggest the disease.
- Staging: Once pancreatic cancer is confirmed, further tests may be done to determine the stage of the cancer, which helps guide treatment decisions. Staging involves assessing the size of the tumor, its extent of spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes, and whether it has metastasized (spread) to distant organs
PANCREATIC CANCER TREATMENT
The treatment of pancreatic cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the location of the tumor, the patient's overall health, and their preferences. Treatment for pancreatic cancer often involves a combination of approaches, which may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. treatment options:
- Whipple Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy): This complex surgery involves removing the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, the gallbladder, and sometimes part of the stomach and nearby lymph nodes.
- Distal Pancreatectomy: In this surgery, the tail and part of the body of the pancreas are removed.
2. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is often used in various stages of pancreatic cancer. It can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor, after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to kill any remaining cancer cells, or in advanced cases to manage the disease and relieve symptoms.
3. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be used alongside surgery or chemotherapy to improve local control of the disease and alleviate symptoms, especially pain.
4. Targeted Therapies: These are drugs that specifically target certain molecules or pathways involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Targeted therapies can be used in combination with chemotherapy or as standalone treatments in some cases.
5. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy works by boosting the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. While it's still being studied for pancreatic cancer, some immunotherapy drugs have shown promise in certain cases.
6. Palliative Care: In cases where the cancer is advanced and cannot be cured, palliative care focuses on improving the patient's quality of life by managing symptoms such as pain, nausea, and digestive issues.
PREVENTION OF PANCREATIC CANCER
No Smoking: Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco consumption is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of developing this disease.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and being overweight are associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce this risk.
- Healthy Eating: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low in processed red meats and high-fat foods may be beneficial in preventing pancreatic cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of several diseases, including pancreatic cancer. Limiting the amount of alcohol consumed can contribute to prevention.
CONCLUSION
Pancreatic cancer remains a significant healthcare challenge, taking a holistic approach that encompasses understanding symptoms, underpinning causes, accurate individual styles, evolving treatment options, and preventative strategies. Public mindfulness, continued exploration and medical advances are pivotal to perfecting early discovery, quality of care and eventually survival prospects for those affected by this complex complaint.
It is characterized by abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells in the lung, forming a malignant tumor. cancers can be divided into two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). In this post we will discuss how to tell if you have NSCLC or SCLC and what treatment options are available for each type.
WHAT IS LUNG CANCER?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cells that make up the lining of your lungs. It’s the most common type of cancer in both men and women, but it can occur at any age. Lung cancer cells grow quickly when they are not being watched, so you need to be aware that there may be signs or symptoms early on if you think you have lung cancer.
Cancer starts when DNA (the building blocks of genes) undergoes changes due to natural causes or bad habits like smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol excessively or exposure to environmental pollutants such as asbestos dust from construction sites etc., which leads to mutation and then abnormal cell growth resulting into tumors (tumors are groups of cells with different characteristics).
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of your body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. The cancer may also start in one part of the lung and then spread to another. If you have lung cancer, it’s important that you see a doctor right away so that they can diagnose and treat it properly.
WHO GETS LUNG CANCER?
Lung cancer is the most common type of cancer in both men and women. It’s also the leading cause of cancer death in both genders. Lung cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs (called carcinoma) grow out of control and can spread to other parts of your body, including your bones or brain (metastatic). There are many risk factors that may increase your chances of getting lung cancer, including:
- Smoking cigarettes
- Exposure to asbestos while working as a construction worker
- Exposure to radon gas during mining activities
Exposure to certain chemicals and fumes in the workplace Exposure to radiation from medical treatments, such as x-rays or CT scans Being male over the age of 55 Having a history of heavy drinking Smoking cigarettes is by far the biggest risk factor for lung cancer. When you inhale cigarette smoke, these chemicals enter your lungs and bloodstream where they can damage DNA and cause cells to grow out of control. The risk of lung cancer increases with the amount of cigarettes smoked each day and the number of years you’ve been a smoker.
HOW IS LUNG CANCER DIAGNOSED?
If you're diagnosed with lung cancer, it's important to know how the disease is diagnosed. To begin with, your doctor will take a physical exam and use various tests to look for any symptoms or signs of lung cancer. They may also perform imaging studies such as X-rays and CT scans to help determine whether or not there's a tumor in your lungs. Your doctor may also order blood tests if they suspect that you have other health conditions (like diabetes) that could be causing symptoms in addition to lung cancer itself—but these are usually just used as part of regular screenings anyway!
They may also order a biopsy of your lungs, which can help them confirm the presence of cancer cells. This involves taking some tissue samples from inside your lungs and sending them to a lab for analysis.The biopsy will tell your doctor if there's a tumor in your lung, as well as whether or not it's cancerous. If the results come back positive, they'll also be able to determine what type of cancer you have and how advanced it is (meaning how far along the disease has progressed).
Once they've diagnosedlung cancer, your doctor will discuss treatment options with you. If it's diagnosed early, lung cancer is usually curable. However, if it's not treated immediately and allowed to spread, it can be fatal. If you're experiencing symptoms of lung cancer, it's important to see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer has helped many patients live longer lives with better quality of life than if they'd waited for their symptoms to worsen.
IS THERE A CURE FOR LUNG CANCER?
The best way to treat lung cancer is with treatment. Unfortunately, there is no cure for lung cancer. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as targeted therapies that target specific proteins in your body’s cells or genes that have been linked to certain types of tumors (e.g., EGFR kinase inhibitors).
While these treatments can help you live longer than those who don't get them—and some people even experience long-term remission after their initial diagnosis—they won't always be successful at curing your disease entirely and may cause side effects like hair loss or nausea during treatment. In some cases, it may also be difficult for family members who care for you because they need time off work due to fatigue or other symptoms caused by the medicines being used during active phases of treatment; however long-term survivors often continue working full time years after diagnosis with minimal interruptionsto their careers.
If you have lung cancer and are interested in learning more about treatment options, our doctors can help. They'll evaluate your situation by reviewing your medical history and performing an exam before discussing a course of treatment that's right for you.
HOW IS LUNG CANCER TREATED?
Early-stage lung cancer is usually treated with surgery and radiation therapy, while advanced-stage lung cancer requires chemotherapy or other therapies. Combination treatments may be used to increase survival rates in some cases of early-stage lung cancers. For example, combining chemotherapy with radiation therapy can kill more cells than either treatment alone without adding side effects like vomiting or hair loss.
Hormone therapy has been shown to improve survival rates among patients with hormone receptor positive (HR+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer cells that have receptors for hormones do not respond normally when these hormones are blocked by medications called aromatase inhibitors such as anastrozole (Arimidex), letrozole (Femara) and exemestane (Aromasin). The medications work by blocking the effects of estrogen on breast cancer cells, which may allow doctors to delay or prevent recurrence. Hormone therapy may also be used as a first-line treatment for women with advanced-stage breast cancer and to reduce the risk of recurrence among patients who have completed surgery, radiation therapy and hormone therapy.
You can ask your doctor or nurse for help with self-care and follow-up appointments. Get information from the pharmacist about how to take medicine safely and how to store it properly. This is important because many medicines can harm your body if they get too hot or cold or are stored in the wrong place (such as on top of a refrigerator).
Talk with a dietitian about what foods are good for your lungs and why certain things make them sicker than others do; this will help keep them healthy overall when eating habits change over time due to illness progression (or remission), which happens often during cancer treatment periods when there's less appetite due physical weakness caused by radiation therapy treatments given before surgery was performed after diagnosis/surgery/chemotherapy done during treatment process(s)/procedure(s) performed immediately following diagnosis/surgery/chemotherapy done during treatment process(s)/procedure(s) performed immediately following diagnosis /surgery/chemotherapy done during treatment process(s)/procedure(s) performed immediately following diagnosis. You may also want to make a note of any foods that cause you to feel worse so that you know what to avoid in the future.
This can help you avoid further complications and make your recovery faster. If you have questions about what types of foods are good for your lungs or what things might be causing them harm, talk with a dietitian who can help guide you in the right direction.
CONCLUSION
It is important to know the symptoms of lung cancer so that you can recognize them early on, when it’s still treatable. If your doctor thinks you have lung cancer, they may recommend a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis before starting treatment. This can help them determine how aggressive your disease is, as well as whether other organs are affected.
Bosom disease is a broad and serious medical problem that influences the two ladies and, in uncommon cases, men. It happens when the cells in the bosom develop wildly, framing a growth. This article intends to give an exhaustive outline of bosom disease, including its causes, side effects, finding, treatment choices, and preventive measures.
Bosom disease is a sort of malignant growth that creates in the bosom cells. It is the most normal disease among ladies overall and is likewise known to influence men, though at a much lower rate. Grasping bosom malignant growth, its causes, side effects, and treatment choices is significant for early identification and successful administration of the infection.
FIGURING OUT BOSOM DISEASE
- 2.1 KINDS OF BOSOM MALIGNANT GROWTH: Bosom malignant growth can be sorted into a few kinds, incorporating ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), obtrusive ductal carcinoma (IDC), obtrusive lobular carcinoma (ILC), and fiery bosom disease (IBC). Each type has unmistakable attributes and requires explicit treatment to draw near.
- 2.2 GAMBLE VARIABLES: Different elements can expand the gamble of creating bosom malignant growth. These incorporate age, orientation, family ancestry, individual history of bosom conditions, certain hereditary changes, hormonal variables, and way of life decisions. While some gamble factors can't be adjusted, for example, age and hereditary inclination, others can be tended to through preventive measures.
- 2.3 HEREDITARY ELEMENTS: A few people acquire quality changes, for example, BRCA1 and BRCA2, which essentially increment their vulnerability to bosom malignant growth. Hereditary testing and advising can assist with recognizing people at high gamble and guide them in coming to informed conclusions about their wellbeing.
- 2.4 HORMONAL ELEMENTS: Hormonal variables, like an early monthly cycle, late menopause, and chemical substitution treatment, can impact the gamble of bosom malignant growth. Estrogen and progesterone receptors assume a critical part in the turn of events and movement of chemical receptor-positive bosom tumors.
SIGNS AND SIDE EFFECTS
Early identification of bosom disease depends on perceiving the signs and side effects. Despite the fact that side effects can shift among people, a few normal pointers include:
- 3.1 PROTUBERANCE OR THICKENING: The presence of another bump or thickening in the bosom or underarm region can be an expected indication of bosom disease. Not all protuberances are dangerous, however, counseling medical services proficient for additional evaluation is fundamental.
- 3.2 CHANGES IN BOSOM SIZE OR SHAPE: Unexplained changes in bosom size or shape, like expanding, shrinkage, or lopsidedness, ought to be examined further.
- 3.3 AREOLA CHANGES: Changes in the areola, like reversal, release, redness, or scaling, may demonstrate a fundamental issue, including bosom disease.
- 3.4 BOSOM AGONY: Bosom torment is a typical side effect experienced by numerous ladies and isn't commonly connected with bosom disease. Nonetheless, assuming the agony endures or is joined by other strange side effects, looking for clinical advice is fitting.
- 3.5 SKIN CHANGES: Changes in the skin surface, for example, dimpling, puckering, or redness looking like an orange strip, can be demonstrative of a fundamental issue, including bosom disease.
DETERMINATION
Diagnosing bosom malignant growth includes a progression of tests and systems to decide the presence, degree, and qualities of the sickness. The symptomatic cycle might include:
- 4.1 BOSOM ASSESSMENT: An actual assessment of the bosoms and the encompassing regions distinguishes any irregularities or expected indications of bosom malignant growth.
- 4.2 MAMMOGRAPHY: Mammography is a typical screening instrument that utilizes X-beams to create itemized pictures of the bosom tissue. It can distinguish early indications of bosom disease before they are observable through actual assessment.
- 4.3 ULTRASOUND: Ultrasound imaging utilizes sound waves to make pictures of the bosom. It can assist with separating between strong masses and liquid-filled pimples, giving important data for determination.
- 4.4 BIOPSY: A biopsy includes the evacuation of a little tissue test from the bosom for lab examination. It decides if a dubious region is harmful or harmless.
STAGES AND VISUALIZATION
Bosom disease is arranged into various stages in view of the size of cancer and its spread to local lymph hubs or different pieces of the body. The stages range from 0 to IV, with higher stages showing a further developed infection. Visualization differs relying on the stage, growth qualities, and individual variables.
TREATMENT CHOICES
The therapy of bosom disease relies upon different variables, including the stage, cancer qualities, and the patient's general well-being. Treatment choices might include:
- 6.1 MEDICAL PROCEDURE: The medical procedure is in many cases the essential therapy for bosom disease. It can include the evacuation of the growth (lumpectomy) or the whole bosom (mastectomy). Now and again, lymph hubs may likewise be eliminated.
- 6.2 RADIATION TREATMENT: Radiation treatment utilizes high-energy X-beams or different kinds of radiation to kill malignant growth cells and therapist cancers. It is ordinarily utilized after a medical procedure to kill any leftover malignant growth cells and diminish the gamble of repeat.
- 6.3 CHEMOTHERAPY: Chemotherapy includes the utilization of medications to kill malignant growth cells all through the body. It very well may be regulated before a medical procedure to shrivel growths or after a medical procedure to obliterate any leftover disease cells.
- 6.4 CHEMICAL TREATMENT: Chemical treatment is fundamentally utilized for chemical receptor-positive bosom diseases. It includes prescriptions that block or impede the chemicals that advance disease cell development.
- 6.5 DESIGNATED TREATMENT: The designated treatment utilizes drugs that explicitly focus on specific atoms or pathways engaged with disease development and movement. It intends to limit harm to sound cells while actually focusing on malignant growth cells.
COUNTERACTION AND CHANCE DECREASE
While the bosom disease can't be totally forestalled, certain way of life decisions and preventive measures can assist with lessening the gamble:
- 7.1 WAY OF LIFE CHANGES: Keeping a sound way of life, including standard activity, keeping a solid weight, restricting liquor utilization, and staying away from tobacco items, can add to decreasing the gamble of bosom disease.
- 7.2 BREASTFEEDING: Breastfeeding has been related to a decreased gamble of bosom disease, both in the mother and the kid. The more extended the length of breastfeeding, the more prominent the defensive impact.
- 7.3 NORMAL ACTIVITY: Taking part in customary actual work, like lively strolling, cycling, or swimming, has been connected to a lower chance of bosom malignant growth. Hold back nothing 150 minutes of moderate-power practice each week.
- 7.4 SOLID EATING REGIMEN: A decent eating regimen wealthy in natural products, vegetables, entire grains, lean proteins, and solid fats can assist with keeping up with general well-being and diminish the gamble of different malignant growths, including bosom disease.
- 7.5 SCREENING AND EARLY IDENTIFICATION: Ordinary bosom malignant growth screening, including mammography and clinical bosom assessments, can support the early recognition of bosom disease when treatment choices are best.
CONCLUSION
Bosom’s malignant growth is a perplexing illness that requires mindfulness, early recognition, and far-reaching treatment. By grasping its causes, side effects, determination, and treatment choices, people can go to proactive lengths to safeguard their well-being and work on their possibilities of fruitful results. Standard screenings, solid way-of-life decisions, and admittance to quality medical care assume a crucial part in fighting bosom malignant growth.
FAQs - FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
9.1 Could men at any point get the bosom disease?
Indeed, albeit intriguing, men can foster bosom disease. The American Malignant Growth Society gauges that around 2,670 new instances of obtrusive bosom disease will be analyzed in men every year in the US.
9.2 At what age would it be a good idea for me to begin evaluating for bosom malignant growth?
The American Disease Society suggests that ladies with a typical gamble of bosom malignant growth start standard mammograms at 40 years old. Nonetheless, it is fundamental to talk with a medical care supplier to decide the most fitting screening plan in light of individual gambling factors.
9.3 Is bosom disease generally genetic?
No, most of the bosom malignant growths are not innate. Around 5-10% of bosom malignant growth cases are related to acquired quality changes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2.
9.4 What are the normal treatment incidental effects?
Treatment incidental effects can shift contingent upon the kind of treatment. Normal aftereffects might incorporate exhaustion, queasiness, balding, changes in craving, and profound trouble. Nonetheless, headways in steady consideration have essentially further developed aftereffect the executives.
9.5 Can bosom disease be totally restored?
As a rule, bosom disease can be dealt with effectively, particularly when distinguished early. Nonetheless, the anticipation relies upon different elements, including the phase of malignant growth, cancer attributes, and individual reaction to therapy. Progressing observing and follow-up care is essential for the long haul of the board and survivorship.